The Benefits of 1031 Exchange Investment Property
Investing in real estate can be a lucrative venture, but navigating tax implications can sometimes be challenging. One strategy that investors often use to defer capital gains taxes is the 1031 exchange. This provision in the Internal Revenue Code allows an investor to sell a property and reinvest the proceeds in a new property without recognizing capital gains.
One of the primary benefits of a 1031 exchange is the ability to defer paying capital gains taxes on the sale of an investment property. By reinvesting the proceeds in a like-kind property, investors can continue to grow their real estate portfolio without being burdened by immediate tax liabilities.
Another advantage of a 1031 exchange is the potential for increased cash flow and appreciation. By swapping out properties strategically, investors can unlock opportunities for higher rental income or property value growth, ultimately enhancing their overall return on investment.
Additionally, a 1031 exchange provides flexibility for investors to diversify their real estate holdings or consolidate properties to better align with their investment goals. This flexibility allows investors to adapt their portfolio over time as market conditions change or investment objectives evolve.
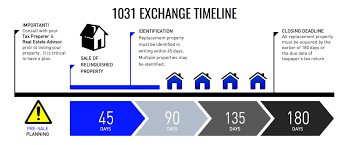
It’s important to note that there are specific rules and timelines that must be followed when conducting a 1031 exchange. Working with qualified intermediaries and real estate professionals who are well-versed in these transactions can help ensure a smooth and successful exchange process.
In conclusion, utilizing a 1031 exchange for investment property offers investors a tax-efficient way to grow their real estate portfolio, increase cash flow and appreciation potential, and maintain flexibility in managing their investments. By taking advantage of this provision in the tax code, investors can maximize their returns and build wealth through strategic real estate investments.
Understanding 1031 Exchange Investment Properties: Key FAQs Answered
- How long do you have to hold an investment property before a 1031 exchange?
- How long do I need to hold properties I use in a 1031 exchange?
- What is 1031 exchange investment property?
- What is the 2 year rule for 1031 exchanges?
- What would disqualify a property from being used in a 1031 exchange?
- Which type of property does not qualify for 1031 exchange?
How long do you have to hold an investment property before a 1031 exchange?
One common question regarding 1031 exchange investment property is, “How long do you have to hold an investment property before a 1031 exchange?” The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) does not specify a minimum holding period for an investment property to qualify for a 1031 exchange. Instead, the focus is on the investor’s intent at the time of purchase. The property must be held for productive use in trade or business or for investment purposes rather than for immediate resale. While there is no strict timeframe requirement, demonstrating a genuine intent to hold the property for investment purposes can help ensure eligibility for a 1031 exchange.
How long do I need to hold properties I use in a 1031 exchange?
When considering properties for a 1031 exchange, a common question that arises is how long one needs to hold these properties to qualify for the exchange. The IRS does not specify a specific holding period; however, the general guideline is that investors should hold the relinquished property and the replacement property for investment purposes rather than for immediate resale. It is recommended to demonstrate an intent to hold the properties for a significant amount of time to meet the requirements of a valid 1031 exchange transaction. Working closely with tax advisors and real estate professionals can provide clarity on individual circumstances and ensure compliance with IRS regulations regarding property holding periods in 1031 exchanges.
What is 1031 exchange investment property?
A 1031 exchange investment property refers to a tax-deferred strategy that allows investors to sell a property and reinvest the proceeds in another like-kind property without incurring immediate capital gains taxes. This provision, named after Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code, enables investors to defer taxes on the appreciation of their real estate holdings, providing an opportunity for continued growth and portfolio expansion. By utilizing a 1031 exchange, investors can maximize their returns, enhance cash flow, and strategically manage their real estate investments while deferring tax liabilities into the future.
What is the 2 year rule for 1031 exchanges?
The 2-year rule for 1031 exchanges refers to the requirement that an investor must hold the replacement property acquired through the exchange for at least two years to qualify for tax deferral benefits. This means that once an investor completes a 1031 exchange by reinvesting the proceeds from the sale of their original property into a like-kind replacement property, they are expected to hold onto the new property for a minimum of two years. Adhering to this rule is crucial in order to comply with IRS regulations and continue deferring capital gains taxes effectively.
What would disqualify a property from being used in a 1031 exchange?
There are specific criteria that a property must meet to qualify for a 1031 exchange, and failure to meet these requirements can disqualify a property from being used in the exchange. Some factors that could disqualify a property include using it as a personal residence or vacation home, acquiring the property for immediate resale rather than for investment purposes, or purchasing foreign real estate. Additionally, properties held for development or as inventory for sale are typically ineligible for 1031 exchanges. It’s crucial for investors to thoroughly understand the IRS guidelines and work closely with professionals experienced in 1031 exchanges to ensure compliance and eligibility of their properties for this tax-deferred strategy.
Which type of property does not qualify for 1031 exchange?
Certain types of property do not qualify for a 1031 exchange. Personal residences, vacation homes, and properties held primarily for personal use are examples of properties that do not meet the like-kind requirement for a 1031 exchange. Additionally, inventory or stock in trade, partnership interests, and certain types of securities are also ineligible for 1031 exchange treatment. It’s important for investors to understand the specific criteria that must be met to ensure that their property qualifies for a successful 1031 exchange transaction.
Tags: 1031 exchange, 1031 exchange investment property, capital gains taxes, holding period, investment goals, investment property, like-kind property, market conditions, property value growth, qualified intermediaries, real estate, rental income, tax implications