The Benefits of Investing in REIT Properties
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) have become a popular choice for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and generate passive income. REIT properties offer several advantages that make them an attractive investment option.
Diversification
Investing in REIT properties allows investors to diversify their portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds. REITs typically own and operate a variety of real estate assets, such as office buildings, shopping centers, apartments, and industrial facilities. This diversification can help reduce risk and protect against market fluctuations.
Passive Income
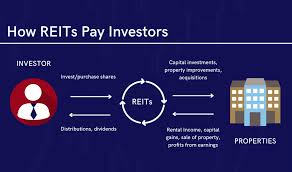
One of the key benefits of investing in REIT properties is the potential for passive income. REITs are required by law to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends. This steady stream of income can provide investors with a reliable source of cash flow.
Liquidity
Unlike owning physical real estate, investing in REIT properties offers liquidity. Shares of publicly traded REITs can be bought and sold on stock exchanges, providing investors with the flexibility to easily enter or exit their positions.
Tax Advantages
REIT properties offer certain tax advantages that can benefit investors. By distributing most of their income to shareholders, REITs are able to avoid paying corporate income tax at the entity level. Additionally, investors may qualify for preferential tax treatment on dividends received from REIT investments.
Professional Management
REIT properties are typically managed by experienced professionals who handle property acquisition, leasing, maintenance, and other operational aspects. This allows investors to benefit from the expertise of seasoned real estate professionals without having to actively manage the properties themselves.
Overall, investing in REIT properties can be a smart way to gain exposure to the real estate market while enjoying benefits such as diversification, passive income, liquidity, tax advantages, and professional management.
Understanding REITs: Key Questions About Real Estate Investment Trust Properties
- How does a real estate REIT work?
- What does REIT property mean?
- Are REITs as good as owning property?
- What is a disadvantage of a REIT?
- Are property REITs a good investment?
- What is better real estate or REITs?
How does a real estate REIT work?
A Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) operates by pooling funds from multiple investors to purchase, manage, and generate income from a portfolio of real estate properties. REITs can own various types of real estate assets, such as commercial buildings, residential complexes, or industrial facilities. By law, REITs must distribute a significant portion of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends. This structure allows individual investors to invest in real estate without directly owning or managing properties themselves. Additionally, REITs are traded on major stock exchanges like regular stocks, providing liquidity and easy access for investors looking to diversify their portfolios with real estate assets.
What does REIT property mean?
A REIT property, short for Real Estate Investment Trust property, refers to real estate assets owned and operated by a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT). REITs are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across various sectors such as commercial, residential, retail, or industrial properties. Investing in REIT properties allows individuals to gain exposure to the real estate market without directly owning physical properties. These properties are typically managed by professionals within the REIT structure and offer investors opportunities for diversification, passive income through dividends, liquidity through publicly traded shares, and potential tax advantages.
Are REITs as good as owning property?
When comparing REITs to owning physical property, it’s important to consider the different characteristics and goals of each investment option. While owning property provides the potential for direct control over the asset and potential appreciation, REITs offer benefits such as diversification, liquidity, professional management, and passive income. REITs can be a more convenient way to invest in real estate without the responsibilities of property management. Ultimately, whether REITs are as good as owning property depends on individual preferences, risk tolerance, and investment objectives.
What is a disadvantage of a REIT?
One common disadvantage of investing in a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) is the potential for volatility in share prices. Like other publicly traded securities, REITs are subject to market fluctuations and can be influenced by factors such as interest rates, economic conditions, and investor sentiment. This volatility can result in fluctuations in the value of your investment and may lead to short-term losses. Additionally, some REITs may carry higher fees or expenses compared to other investment options, which can impact overall returns. It’s important for investors to carefully assess their risk tolerance and investment goals when considering REITs as part of their portfolio.
Are property REITs a good investment?
Investing in property REITs can be a wise financial decision for many investors. Property REITs offer a unique opportunity to gain exposure to the real estate market without the need for direct ownership of physical properties. With their potential for steady income through dividends, diversification benefits, liquidity, and professional management, property REITs can be a good investment option for those seeking passive income and portfolio diversification. However, as with any investment, it is essential for investors to conduct thorough research, consider their financial goals and risk tolerance, and seek advice from financial professionals before making any investment decisions in property REITs.
What is better real estate or REITs?
When considering whether to invest in traditional real estate or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), it ultimately depends on individual preferences, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Investing in physical real estate offers the potential for direct ownership and control over the property, allowing for customization and potential appreciation. On the other hand, REITs provide investors with a more liquid and diversified exposure to the real estate market without the responsibilities of property management. REITs also offer passive income through dividends and may provide tax advantages. Both options have their own merits, so investors should carefully assess their objectives and consider factors such as time commitment, capital requirements, and market conditions before making a decision between real estate or REIT investments.
Tags: benefits, diversification, investing, liquidity, passive income, professional management, properties, real estate, reit, reit property, tax advantages